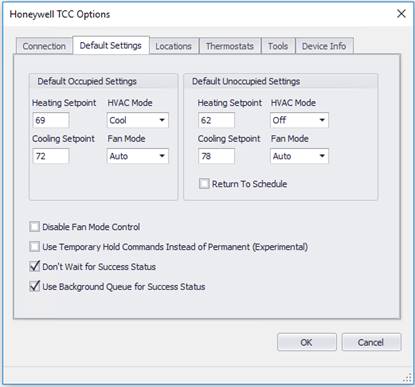
The Default Settings tab shows various default settings and parameters for a thermostat. These settings can be used for each thermostat, or individual settings can be applied to each thermostat.

Default Occupied Settings
These settings are filled in for occupied state when a new
thermostat action is defined and are used when Use Global Occupied
Settings is checked for a thermostat.
|
Field Name |
Description |
Range |
|
Heating Setpoint |
Default setting for the heating setpoint during occupied mode. |
Default = 69 |
|
Cooling Setpoint |
Default setting for the cooling setpoint during occupied mode. |
Default = 72 |
|
System Mode |
Default setting for the system status during the occupied mode. |
Default = Cool AutoCool, AutoHeat, Off, Cool, Heat |
|
Fan Mode |
Default setting for the fan mode status during occupied mode. |
Default=Auto Auto, On |
Default Unoccupied Settings
These settings are filled in for unoccupied state when a
new thermostat action is defined.
|
Field Name |
Description |
Range |
|
Heating Setpoint |
Default setting for the heating setpoint during unoccupied mode. |
Default = 62 |
|
Cooling Setpoint |
Default setting for the cooling setpoint during unoccupied mode. |
Default = 78 |
|
System Mode |
Default setting for the system status during the unoccupied mode. |
Default = Cool AutoCool, AutoHeat, Off, Cool, Heat |
|
Fan Mode |
Default setting for the fan mode status during unoccupied mode. |
Default=Auto Auto, On, FollowSchedule** |
|
Return to Schedule* |
Checked will return the thermostat back to the scheduled setpoints. (FanMode and SystemMode will not follow schedule and should be commanded) |
Default =Unchecked |
* If you enable Return to Schedule, you should program all your scheduled periods as unoccupied so that setpoints are return to unoccupied settings after the event is over.
** Not all thermostats allow “FollowSchedule” fan mode.
Disable Fan Mode Control
In most cases, fan mode settings will remain the same for both occupied and unoccupied modes. If this is the case, selecting this will prevent the additional request needed to command the fan mode.
Note: If you have thermostats with different options and settings, your global settings might be invalid for those different thermostats. (e.g. one thermostat has heating only, and the rest have heating/cooling).
Use Temporary Hold Commands Instead of Permanent (Experimental)
If unchecked (default), a permanent hold command is sent for occupied and unoccupied control (unless “Return to Schedule” is used.
If checked, a temporary hold is sent with a “Hold Until” command set to the next scheduled command. This will allow a backup schedule in the thermostat to become active if the next command never gets sent (due to loss of communications). The thermostat display will also show how long the current setpoints will remain in effect.
Note: The temporary hold feature has not had a lot of testing so use this at your own risk. Not all thermostats support the “Hold Until” temporary hold feature.
Don’t Wait for Success Status
If unchecked, each command sent to the thermostat will wait until either the task status = “Success” or if the “Success timeout” occurs.
If checked (default), once the command is queued to Honeywell’s portal, the task is assumed that it will eventually command the thermostat. This frees up the command queue thread for other commands instead of waiting for the success timeout. If “Use Background Queue for Success Status” flag is checked, the status will be checked for final completion.
Use Background Queue for Success Status
If checked (default), each command sent to the thermostat will be queued to Honeywell and the command task will be tracked in a background queue process until a success/failure or a timeout occurs. If it fails to complete, the original command will be flagged as an error and users will be notified.