This action will execute a PowerShell script based on triggered events from the event provider’s scheduled events.
This action applies to the following event triggers:
•EventStart, EventStop
•EventStartStop
•EventSetupStart, EventSetupStop
•EventSetupTeardown
•EventTeardownStart, EventTeardownStop
•ZoneFirstLastEventStartStop
•ZoneFirstLastSetupTeardown

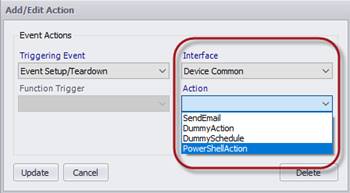
After adding a new action in equipment manager, select one of the triggering events, along with the “Device Common” interface, followed by the “PowerShell” action.
Note: Only the event triggers shown can be used for PowerShell action. The action won’t be available if other event triggers are selected here.
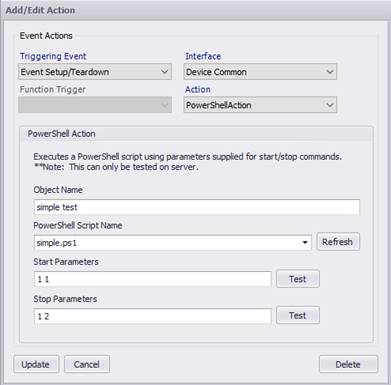
Action Settings
The action dialog allows you to select the PowerShell script to run and the parameters to pass into it.
|
Field Name |
Description |
Range |
|
Object Name |
Unique friendly name for the device under control. |
n/a |
|
PowerShell Script Name |
Name of PowerShell script file to run. |
Only files in <<application root>>\powershell folder will be shown. |
|
Start Parameters |
Arguments to pass into PowerShell script file before running. Executes on the start trigger. |
Depends on script. |
|
Stop Parameters |
Arguments to pass into PowerShell script file before running. Executes on the stop trigger. |
Depends on script. |
Refresh Button
Refreshes the list of available PowerShell script files. This list is populated from the \powershell folder located in the application root directly (C:\program files (x86)\Streamside Solutions\Events2HVAC\powershell)
Test Button
To execute the script for the start or stop command click on the test button. If the script runs w/o errors, a success dialog will be shown. If the script writes a response message to a variable called “$E2HResult” after running, this message will also be displayed.
If an exception is thrown or some other error occurs, that message will be shown in a failure dialog.
Note: The script must be able to run without any user interaction. If the test run doesn’t have permission, you will need to change your execution policy of the local machine.
PowerShell References:
•https://devblogs.microsoft.com/scripting/what-is-powershell/
•https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/scripting/overview?view=powershell-6
PowerShell Command References:
PS>$PSVersionTable.PSVersion
Shows current PowerShell Version
PS>Get-ExecutionPolicy -List
List current execution policy.
PS>Set-ExecutionPolicy policyName
Sets the execution policy for the local machine